Blog > Data Analytics > What is Power BI & Why SQL and Tableau Makes You Better at It
What is Power BI & Why SQL and Tableau Skills Make You Better at It
Quick Answer: What is Power BI and Why is it Important?
Power BI is a business intelligence and data visualisation tool created by Microsoft. Its main purpose is to take raw data from various sources and transform it into interactive, easy-to-understand dashboards and reports. Think of it as a powerful version of Excel charts, but with the ability to connect to live data, create complex visualisations, and share insights across an organisation.
It is important because it makes data analytics accessible to a wider audience beyond just data scientists and IT professionals. Business users, marketers, and managers can use Power BI’s user-friendly interface to monitor performance, spot trends, and make data-driven decisions without needing to write code.
However, to truly master Power BI and become a valuable data analyst, you need a strong foundation in two key areas: SQL to extract and prepare the right data, and data visualisation principles (best learned through a comprehensive tool like Tableau) to create meaningful and effective dashboards. Without these foundational skills, you are only scratching the surface of what Power BI can do.

What is Power BI?
In today’s data-driven world, companies are drowning in information. From sales figures and marketing campaign results to customer feedback and operational metrics, the amount of data available is overwhelming. The challenge isn’t collecting data; it’s understanding it. This is where Power BI comes in.
Power BI is Microsoft’s flagship business intelligence (BI) and data visualisation platform. It is a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to turn your unrelated sources of data into coherent, visually immersive, and interactive insights. At its core, Power BI allows you to easily connect to your data, model it, and then visualise it in a way that is easy to understand and share.
Think of it as the bridge between raw, messy data and clear, actionable business decisions. It allows you to create reports and dashboards that can be updated in real-time, giving you a live pulse on your business.
Power BI is not a single application but a suite of tools that includes:
- Power BI Desktop: A free, downloadable application for your computer where you connect to data, transform it, and build reports.
- Power BI Service: A cloud-based service (SaaS – Software as a Service) where you can publish your reports, create dashboards, and share them with others.
- Power BI Mobile: A mobile app for viewing and interacting with your reports and dashboards on the go.
Because of its user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface and its deep integration with other Microsoft products like Excel and Azure, Power BI has become one of the most popular business intelligence tools in the world.
Why is Power BI Important for Data Analytics?
Power BI has fundamentally changed the landscape of data analytics, moving it from the exclusive domain of IT departments to the desktops of business users everywhere. Its importance stems from several key factors that make it an indispensable tool for modern businesses:
- It democratises data. Before Power BI, creating a business report was a lengthy process requiring a formal request to the IT team. Now, a marketing manager can build their own performance dashboard in an afternoon, empowering teams to make faster, more informed decisions.
- It provides real-time insights. Unlike traditional reports that are outdated once printed, Power BI dashboards can connect to live data sources. This provides an up-to-the-minute view of operations, which is crucial for fast-paced industries like e-commerce and finance.
- It integrates seamlessly with the Microsoft ecosystem. For companies already using Microsoft 365, Azure, and SQL Server, Power BI fits perfectly into their existing workflows, allowing for easy data transfer and collaboration.
- It is incredibly cost-effective. The Power BI Desktop application is completely free, allowing anyone to start learning. The cloud-based service also offers a free tier, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- It has widespread industry adoption. A vast majority of Fortune 500 companies use Power BI, and it is consistently ranked as a leader in the analytics space by industry analysts like Gartner [1]. This makes it a valuable and expected skill for any data professional.
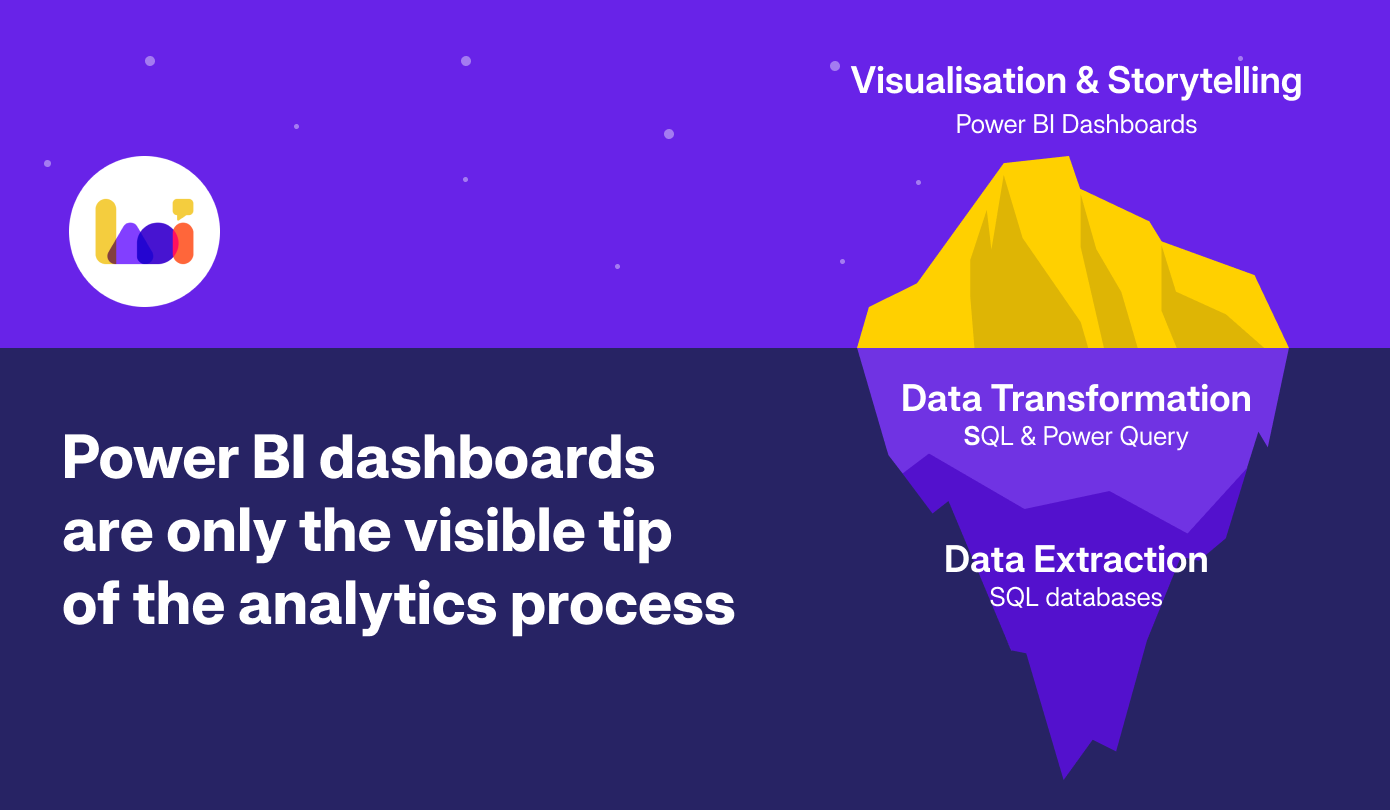
The Foundation Power BI is Built On
Power BI is an incredibly powerful tool, but it’s important to understand that it is the final layer in the data analytics process—the presentation layer. Like the tip of an iceberg, the beautiful dashboards you see are only possible because of the foundational work that happens beneath the surface.
To use Power BI effectively, you need to master the skills that power it. This foundation can be broken down into three essential layers.
1. Data Extraction (The Role of SQL)
Before you can visualise any data, you must first get it from a database. This is where SQL (Structured Query Language) comes in. SQL is the universal language for communicating with databases. While Power BI has connectors that can link to various data sources, you still need to tell it what data to pull.
For example, if your manager asks for a dashboard showing sales performance for the last quarter in the Asia-Pacific region, you can’t just point Power BI to your company’s massive sales database. You need to write a SQL query to extract only the relevant data.
Without SQL, you are limited to using pre-prepared, static datasets (like Excel files), which severely limits your ability to perform real-time, ad-hoc analysis. Mastering SQL gives you the freedom to access and analyse any data you need, making you an independent and resourceful analyst.
2. Data Transformation (SQL and Power Query)
Raw data is almost never ready for analysis. It’s often messy, incomplete, or in the wrong format. The process of cleaning, shaping, and preparing data is known as data transformation. This is arguably the most critical and time-consuming part of a data analyst’s job.
While Power BI has a built-in tool called Power Query for this, the logic behind it is heavily based on SQL principles. Operations like joining tables, filtering out irrelevant information, and aggregating data are all fundamental SQL concepts.
Knowing SQL makes you exponentially faster and more effective at data transformation. You can perform complex data preparation steps directly in your SQL query before the data even enters Power BI, resulting in faster dashboards and more efficient workflows.
3. Visualisation Design (Data Storytelling Principles)
Once you have clean data, the final step is to visualise it. This is more than just dragging and dropping fields onto a canvas. It’s about telling a clear and compelling story with your data. This involves understanding data visualisation principles: choosing the right chart for your message, designing an intuitive dashboard layout, and guiding your audience to the key insights. These principles are universal and apply to any visualisation tool, whether it’s Power BI, Tableau, or Google Data Studio.
At Heicoders Academy, we believe in building a strong foundation. Our DA100: Data Analytics with SQL and Tableau course is designed to give you these three foundational layers. Our students consistently report that after mastering SQL and data visualisation principles with Tableau, they can pick up Power BI on the job with remarkable ease, because they understand the thinking behind the tool.
Why Learning Tableau Makes You Better at Power BI
This might sound counterintuitive, but one of the best ways to become an expert at Power BI is to first learn its main competitor, Tableau. While they are different products, they are both built on the same fundamental principles of data visualisation. By learning one, you are implicitly learning the core concepts of the other.
Think of it like learning to drive a car. If you learn to drive a Toyota, you can easily get into a Honda and figure it out in minutes. The steering wheel, pedals, and basic controls are the same. The same is true for data visualisation tools. The skills you gain in Tableau are directly transferable to Power BI.

What You Learn in Tableau That Applies to Power BI
- Visualisation Best Practices: In Tableau, you learn when to use a bar chart versus a line chart, a scatter plot versus a heat map. This knowledge is universal and is crucial for creating effective dashboards in Power BI.
- Dashboard Design: You master the art of dashboard layout, creating interactive filters, and designing a user experience that is both intuitive and insightful. These design principles are identical in Power BI.
- Data Storytelling: You learn how to arrange your visualisations to tell a compelling story that guides your audience to a conclusion. This is a critical skill that has nothing to do with the specific tool you are using.
- Calculated Fields: The logic used to create calculated fields in Tableau is very similar to the logic used in Power BI’s DAX (Data Analysis Expressions). Once you understand how to create calculations in one tool, the other becomes much easier.
The Advantage of Learning Tableau First
Many data professionals believe that learning Tableau first provides a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of data visualisation. Tableau is often considered more powerful and flexible for complex visualisations, which forces you to think more deeply about your design choices. Once you have mastered the more robust tool, a simpler tool like Power BI becomes incredibly intuitive.
A Real Student’s Perspective: Don’t just take our word for it. Here’s what one of our DA100 graduates, Mei Hoon Ang, said in her 5-star Google review:
“If you’re serious about learning data analytics—particularly SQL and Tableau—Heicoders Academy is the place to be. The course is very well-structured, starting with the fundamentals… I would strongly recommend Heicoders Academy to anyone looking to build a solid foundation in data analytics… what I’ve learned here will definitely serve as a strong base for me to continue building upon.”
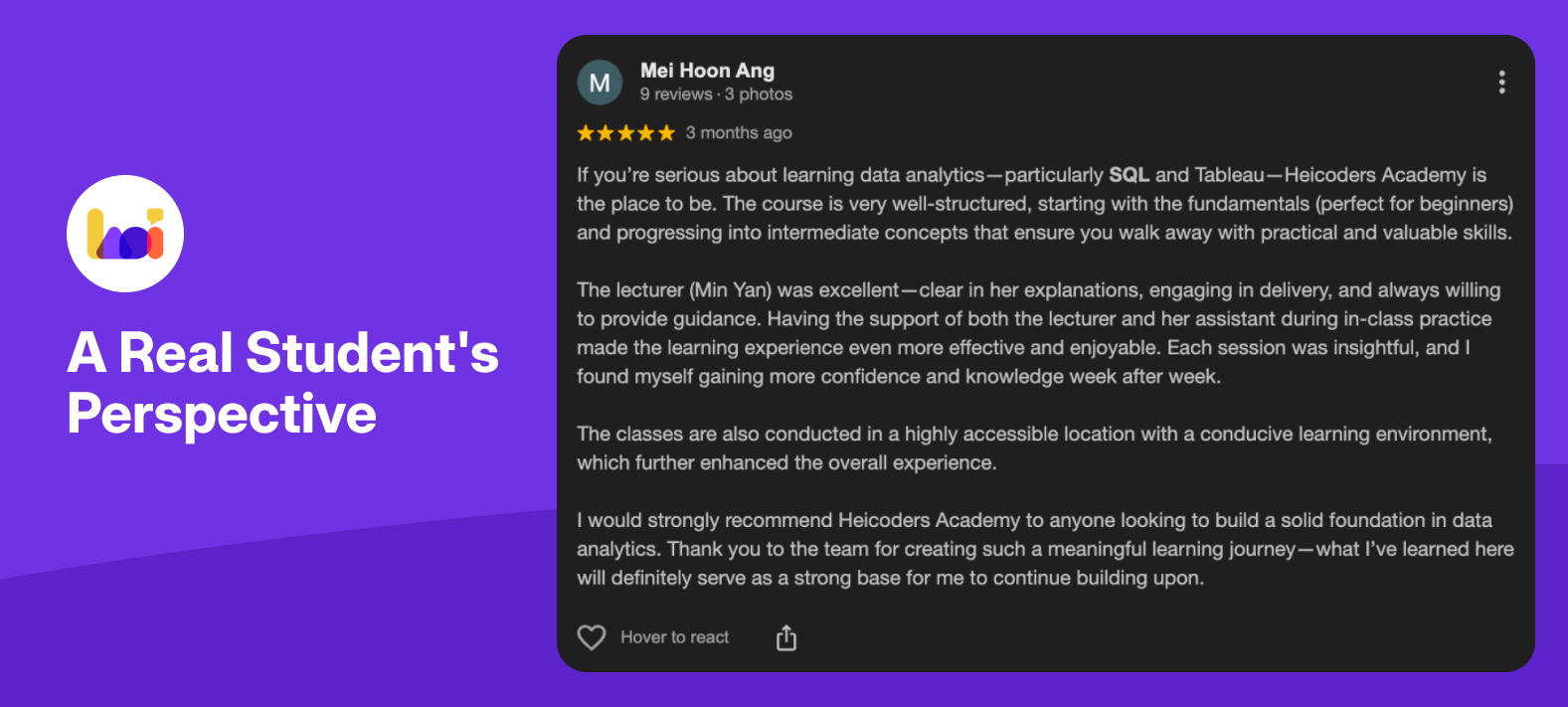
Mei Hoon’s experience highlights a crucial point: mastering the fundamentals of SQL and data visualisation principles is the key to long-term success. Once you have that strong base, you can confidently tackle any tool, including Power BI.
This is why we teach Tableau in our DA100 course. It provides the most robust and comprehensive foundation in data visualisation, equipping our students with the skills to master Power BI or any other tool they encounter in their careers.
SQL: The Universal Skill Behind Every Power BI Dashboard
You can learn the Power BI interface in a week. You can memorise where the buttons are and how to create a bar chart. But without SQL, you will never be more than a button-clicker. SQL is what separates a casual Power BI user from a professional Power BI expert.
Why SQL is Non-Negotiable for Power BI Mastery
Data Extraction is Everything: Power BI is a visualisation tool; it is not a database. To build any meaningful report, you first need to get data from a database. SQL is the only way to do that. It allows you to select the exact columns and rows you need, filter out irrelevant information, and perform calculations before the data even enters Power BI.
The 80/20 Rule of Data Analytics: In the real world, data analysts spend about 80% of their time preparing data and only 20% of their time visualising it. Data preparation—joining tables, cleaning messy data, and creating new fields—is all done with SQL or SQL-based logic.
Performance is Key: If you pull an entire 10-million-row table into Power BI and then try to filter it, your dashboard will be incredibly slow. An expert analyst writes an efficient SQL query to pull only the 10,000 rows they need, resulting in a fast and responsive dashboard.
You Are Not Limited by the Interface: Every tool has its limitations. There will be times when Power BI’s drag-and-drop interface can’t perform the complex transformation you need. With SQL, you are never limited. You can always write a query to shape the data exactly how you need it.
At Heicoders Academy, we start with SQL in our DA100 course because it is the bedrock of data analytics. We believe that teaching our students to write SQL queries before they even touch a visualisation tool is the single most important factor in their career success.
The Right Learning Path for Power BI Mastery
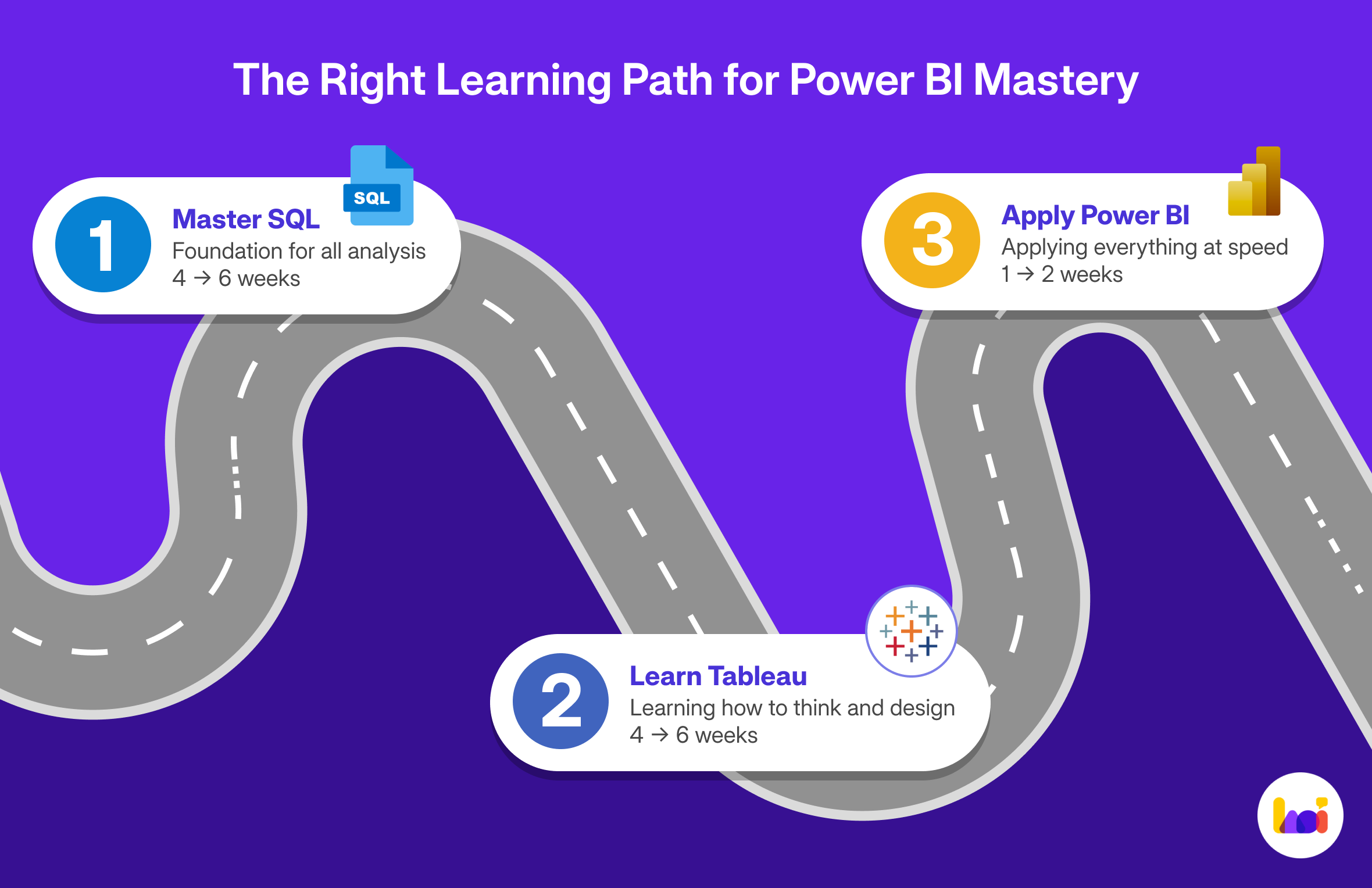
If you are serious about a career in data analytics, it is crucial to learn skills in the right order. While it might be tempting to jump straight into a flashy tool like Power BI, this is like trying to build a house by starting with the roof. A strong foundation is essential for long-term success. Here is the learning path that we have seen work for our students:
Step 1: Master SQL (The Foundation)
Before you do anything else, learn SQL. This is the most important skill for any data analyst. Focus on understanding how to query databases, join tables, aggregate data, and write subqueries. A solid 4-6 weeks of structured learning in SQL will set you up for success in everything that follows.
Step 2: Learn Data Visualisation Principles (with Tableau)
Next, learn the art and science of data visualisation. We recommend learning this with Tableau because its flexibility encourages a deeper understanding of visualisation principles. Focus on dashboard design, user experience, and data storytelling. This will take another 4-6 weeks of dedicated practice.
Step 3: Apply Your Skills to Power BI
Once you have a strong foundation in SQL and data visualisation, learning Power BI becomes trivial. You will find that you can pick up the interface in just a few days. The core concepts are the same, and your foundational knowledge will allow you to use Power BI at a much deeper level than someone who started with it. You can spend 1-2 weeks learning the specifics of Power BI, and you will be more effective than someone who has spent months only using that one tool.
This is the exact progression we follow in our DA100 course. We have seen this path consistently produce top-tier data analysts who are not just tool users, but true data professionals.
Power BI Skills in Singapore: What Employers Really Want
In the competitive Singapore job market, having “Power BI” on your resume is a good start, but it’s not enough to land you the job. Employers are looking for candidates with a deep understanding of the entire data analytics workflow, not just familiarity with one tool.
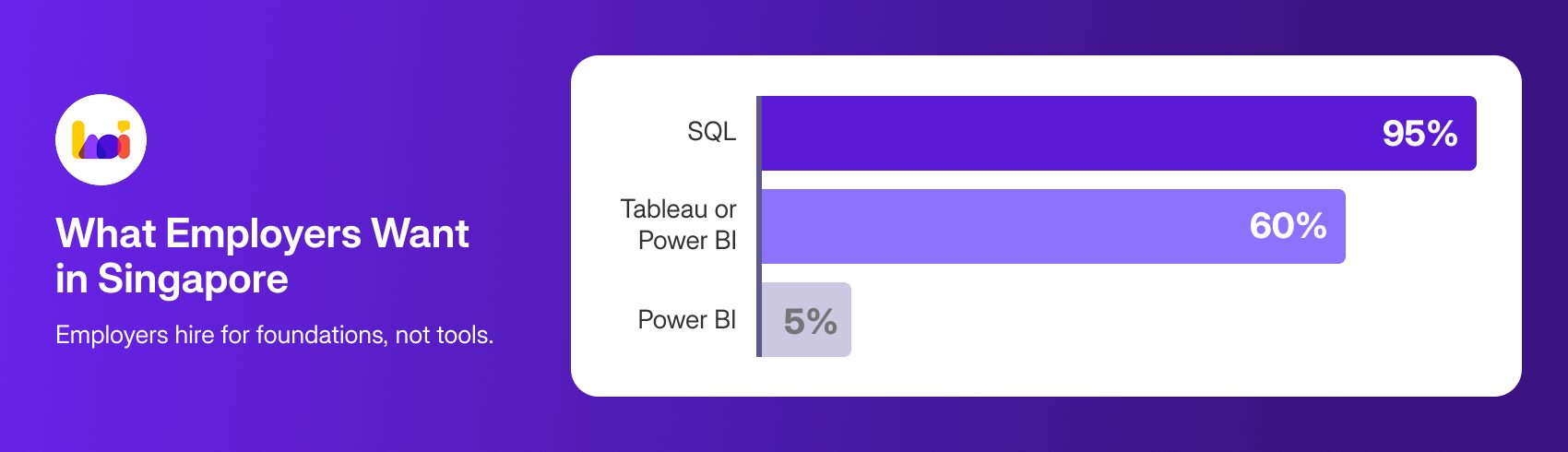
We analysed over 100 data analyst job postings on LinkedIn and MyCareersFuture in Singapore. Here’s what we found:
- 95% of data analyst jobs required proficiency in SQL.
- 60% mentioned a visualisation tool, with the requirement often being “Tableau or Power BI”.
- Only 5% required Power BI specifically without also mentioning SQL.
The message from employers is clear: SQL is non-negotiable, while the specific visualisation tool is often interchangeable.
This sentiment is common among hiring managers. A typical perspective in the industry is that it’s easier to teach a new hire a specific tool like Power BI than it is to teach them the foundational principles of data analysis and SQL. A common refrain you might hear is, “We can teach a new hire Power BI in a week. We can’t teach them analytical thinking and SQL that fast. We hire for the foundation, not the tool.”
This is why our DA100 graduates are so successful in the job market. They are hired because they have the strong, transferable foundation that employers are desperately looking for.
Real-World Power BI Use Cases (And the SQL Behind Them)
Let’s look at some common Power BI dashboards and see how SQL and visualisation principles are the real stars of the show.
Use Case 1: Sales Dashboard
- What it shows: A dashboard with charts for revenue by region, top-selling products, and salesperson performance.
- The SQL behind it: A query that JOINs the sales, products, customers, and employees tables, FILTERs for the correct date range, and GROUPs the data by region and product.
- The Tableau principle: Using bar charts for comparisons, a map for regional data, and a table for detailed salesperson metrics.
- Power BI’s role: Providing the user-friendly interface to assemble these visualisations.
Use Case 2: Marketing Analytics Dashboard
- What it shows: A funnel visualisation of a marketing campaign, from impressions to conversions, along with ROI calculations.
- The SQL behind it: A series of complex JOINs across campaigns, clicks, and conversions tables, along with calculated fields for conversion rates and ROI.
- The Tableau principle: Knowing that a funnel chart is the best way to visualise this process and designing it for clarity.
- Power BI’s role: Connecting to live data from Google Analytics or other marketing platforms.
In every case, the pattern is the same. The impressive Power BI dashboard is the final output, but the real analytical work happens in the SQL query and the visualisation design phase.
FAQs: Your Power BI Questions Answered
1. Is Power BI free?
Yes, the Power BI Desktop application is completely free to download and use. The cloud-based Power BI Service, which is required for sharing and collaboration, has both a free tier and paid “Pro” and “Premium” licences.
2. Do I need coding skills to use Power BI?
No, you don’t need traditional programming skills like Python or Java. However, to use Power BI effectively in a professional setting, you absolutely need SQL.
3. Should I learn Power BI or Tableau first?
We strongly recommend learning SQL first, then a comprehensive visualisation tool like Tableau. With that foundation, learning Power BI will be quick and easy.
4. Can I get a job with just Power BI skills?
It is highly unlikely. Employers hire data analysts, not Power BI operators. They expect you to have strong SQL skills and a solid understanding of data analytics principles.
5. How long does it take to learn Power BI?
You can learn the basics of the Power BI interface in 1-2 weeks. However, mastering it to a professional level requires a strong foundation in SQL and data visualisation, which takes 8-12 weeks of structured learning.
6. Is Power BI better than Tableau?
Neither is definitively “better.” They have different strengths. Power BI excels in its integration with the Microsoft ecosystem and its user-friendly interface. Tableau is often considered more powerful for complex, custom visualisations. Both require SQL and data thinking to be used effectively.
7. Do I need to learn SQL before Power BI?
Yes. We cannot stress this enough. For any serious, real-world application of Power BI, SQL is an essential prerequisite.
8. What is the best way to learn Power BI in Singapore?
The best way is to first build a strong foundation. Instead of looking for a “Power BI course,” look for a comprehensive data analytics course that teaches SQL and data visualisation principles. Our DA100 course is designed to do exactly that.
Master Power BI by Building the Right Foundation
Power BI is a fantastic and powerful tool that has a well-deserved place in the modern data analytics toolkit. It is user-friendly, cost-effective, and deeply integrated with the business software that runs the world.
However, it is crucial to remember that Power BI is just that, a tool. It is the final step in a long process of data extraction, transformation, and analysis. The most beautiful dashboard is useless if it is built on the wrong data or communicates a misleading message.
At Heicoders Academy, we are committed to teaching you how to think like a data analyst, not just how to use a specific piece of software. We believe that the path to mastering Power BI or any other tool you will encounter in your career starts with a rock-solid foundation in SQL and data visualisation principles.
Our DA100: Data Analytics with SQL and Tableau course is designed to give you that foundation. We start with SQL, the universal language of data. We then teach you the art and science of data visualisation with Tableau, a tool that encourages deep thinking and creativity.
Furthermore, learning Data Analytics with Heicoders is not just about mastering SQL and Tableau. We teach you how to think like a senior data analyst. Even with all the technical skills in the world, if you don’t have the right analytical mindset, you won’t be able to derive useful conclusions and actionable insights for your organisation.
Our curriculum is designed to build this critical thinking, ensuring you can not only answer questions with data but also know which questions to ask in the first place. Our graduates leave not as “Tableau users,” but as data professionals who can confidently tackle any analytics challenge, whether the final output is in Tableau, Power BI, or any other tool.
If you are ready to build the foundation that will make you a true Power BI expert and a highly sought-after data analyst, we invite you to explore our DA100 course. Join over 10,000 skilled learners who chose to learn the right way.

Upskill Today With Heicoders Academy
Secure your spot in our next cohort! Limited seats available.

