Blog > Data Science & AI > What is Machine learning? Why is it Important?
What is Machine Learning? Why is it Important?
What is Machine Learning? Why is it Important?
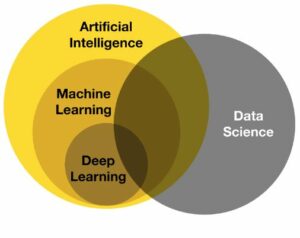
Credits: Machine learning vs Artificial Intelligence
To provide you with a basic intuition of what machine learning entails, machine learning is what powers some innovative products that we know and love today, such as Netflix’s recommendation engine or self-driving cars.
In their 2021 survey, PricewaterhouseCoopers revealed that 86% of participants regarded AI technology as a mainstream part of their company; with more than 52% also accelerating adoption plans for Machine Learning to improve the circumstances created by Covid-19. Fortune Business Insights valued the global Machine Learning market to be worth USD$21.17 billion in 2022 and estimates a whopping growth of almost tenfold to USD$209.91 billion by 2029.
Even in these ‘early days’, we are seeing the impact of Machine Learning methods being used to great success. Yelp presents the most accurate information from credible reviews through automated image curation. Pinterest got a boost from its acquisition of Kosei in 2015, using the company’s B2B Machine Learning capabilities to guard against spam, provide better monetisation of ads, and offer exciting customised discovery to its users.
Tesla is making waves on the road by processing video imagery through rich algorithms to deliver auto-pilot transportation. As big data and its use cases continues to expand, so will the market demand for data scientists and data analyst. Hence, now is a better time than ever to make your first foray into machine learning.
How are organisations using Machine Learning?
Here we share 2 classical type of problems which companies / organisations apply machine learning in:
1. Regression problems
Regression problems describes a situation where we we are trying to get a regression machine learning model model to learn from data, and thereafter predict for an outcome that has a continuous value (essentially numbers with decimal places) such as: BMI, stock price and sale price of a house.
One of the more interesting use case of regression model is in the area of ride-hailing. Ride-hailing companies make use of regression machine learning model to predict the customer lifetime value of its customers. In this way, they can then further deduce which customers are worth providing vouchers and incentives to keep them locked in the ecosystem.
2. Classification problems
Classification problems entails training a classification machine learning model model to learn from data, and thereafter predict for an outcome that has a categorical value (discrete outcomes) such as: whether someone has diabetes or not. Interestingly, 70-80% of the applications of machine learning in business problems are classification problems in nature.
One example where classification models are used involves – Global energy giant Shell. When faced with a growing pressure to be more sustainable, Shell tapped into historical data to guide efficient and less damaging precision drilling. As charging stations become the norm, the oil and gas company also studies consumer usage to map out future developments, as well as plan their grids. Machine Learning even takes place in computer cameras installed at these stations, which detect dangerous activity or items (such as the lighting of a cigarette) to alert staff of potential danger.
Other brands like Paypal use it to observe ethical transactions to detect fraud. LinkedIn produces relevant news feeds for its users, and attempts to make connections between employers and candidates – a core prong in their business.
Career Opportunities
Behind this data revolution are a whole host of data engineers, data scientists, and Machine Learning engineers. Yes – even though the machine learning models are very much executed by computers, the models themselves were built by people.
Data engineers are responsible for createing data databases to ingest, store, transform and distribute data in accordance with business needs. The data scientist role is more research-focused in nature, and it usually involves cleaning and studying the data, and thereafter build the machine learning models in accordance with the business problems. Machine Learning engineers can be thought of as an extension of data scientist – whereby they do what a data scientist does, but also go on to operationalise the models that will ultimately be used by clients.
While a career transition into a new specialisation can be dauting, here is where courses such as AI200: Applied Machine Learning from Heicoders Academy help you achieve that career transition.
For beginners with no programming background, you can start off with our foundation course: AI100: Python Programming and Data Visualisation. In this course, learners can expect to learn data wrangling and generate graphic visualisation that help inform business decisions.
Secure your future in Machine Learning with specialised courses from Heicoders Academy.

Upskill Today With Heicoders Academy
Secure your spot in our next cohort! Limited seats available.
